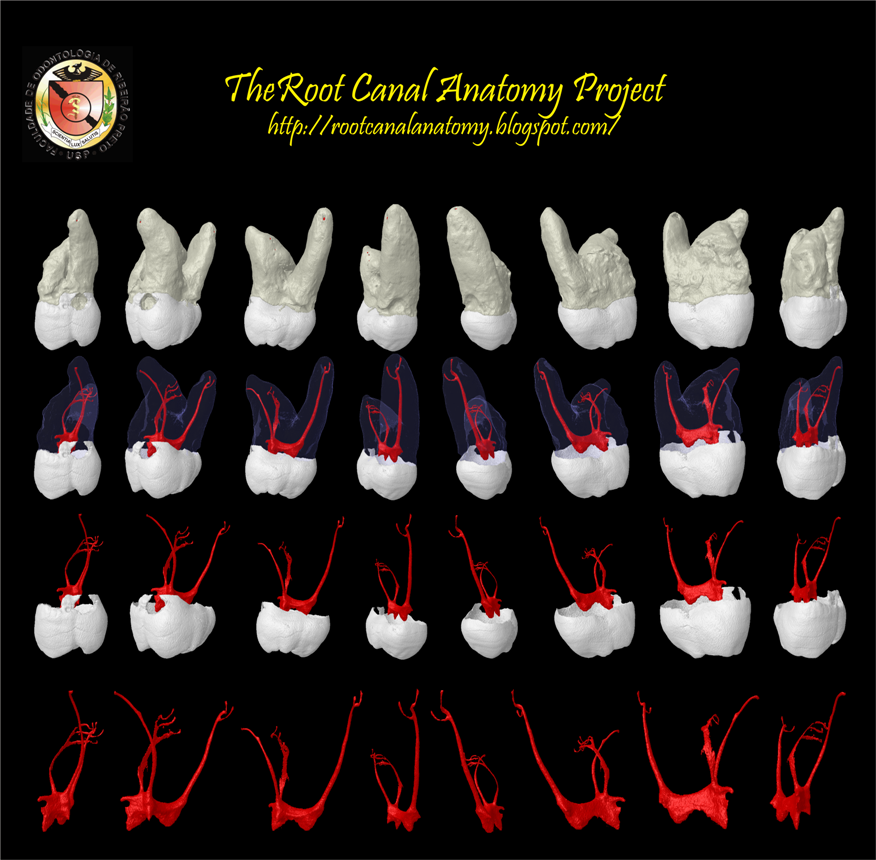
The Root Canal Anatomy Project Maxillary First Molar
- objectives of Endodontic Convenience form 1. unobstructed access to the canal orifice 2. direct access to the apical foramen - freedom within coronal cavity to reach apex in unstrained position 3. cavity expansion to accommodate filling techniques 4. complete authority over enlarging instrument
The Root Canal Anatomy Project Maxillary First Molar
As the complex anatomy of maxillary first molars is one of the major challenges in endodontic therapy, knowledge of the complicated root canal anatomy and configuration is crucial to ensure the success of endodontic treatment and prognosis.
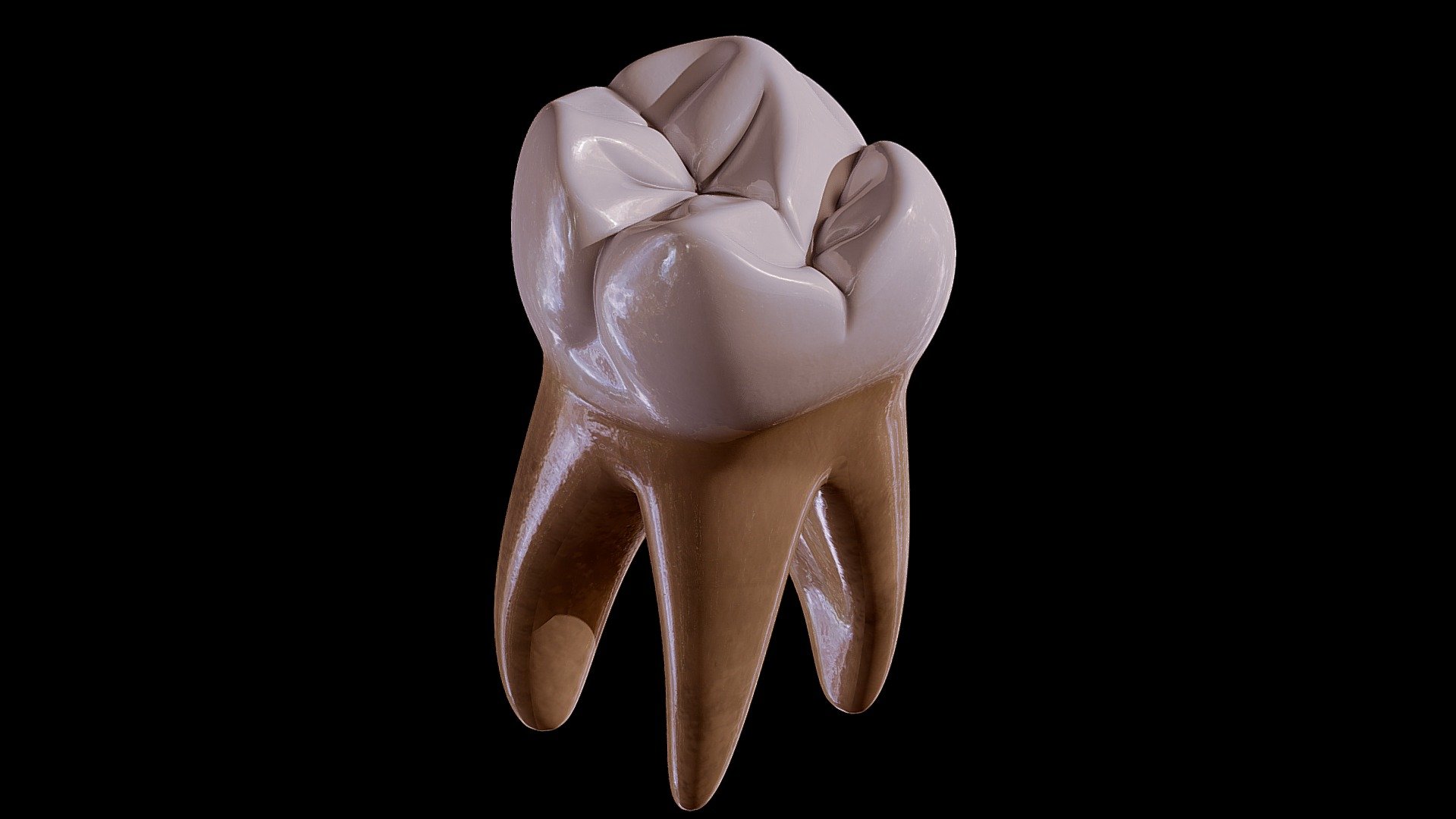
Printable Tooth (Maxillary First Molar) Buy Royalty Free 3D model by Rossty (rossty05
1.2 Root morphology. Among the maxillary teeth, the permanent first molar has the strongest anchorage in the maxillary arch due to their well-developed widely separated roots [].Typically, this tooth has three roots, the mesiobuccal, distobuccal, and palatal [].These roots diverge in a manner parallel to the direction of the maximum force that could be applied diagonally against the crown in a.

The Root Canal Anatomy Project Maxillary First Molar
Maxillary first molars are generally three-rooted with four root canals (Fig. 4.13 ). The additional canal is located in the mesiobuccal root. The canal form of the mesiobuccal root has been extensively investigated.

3d model maxillary molar
First molars are missing in one-third of the cases, the second molars in almost all the cases and the wisdom teeth are always missing.. Further, the maxillary first premolars presented a 3.2 mm extrusion. 86 The second premolars were extruded 1.9 mm according to Brickman et al, 87 while in contrast Haydar & Uner found 1.9 mm of intrusion. 88.
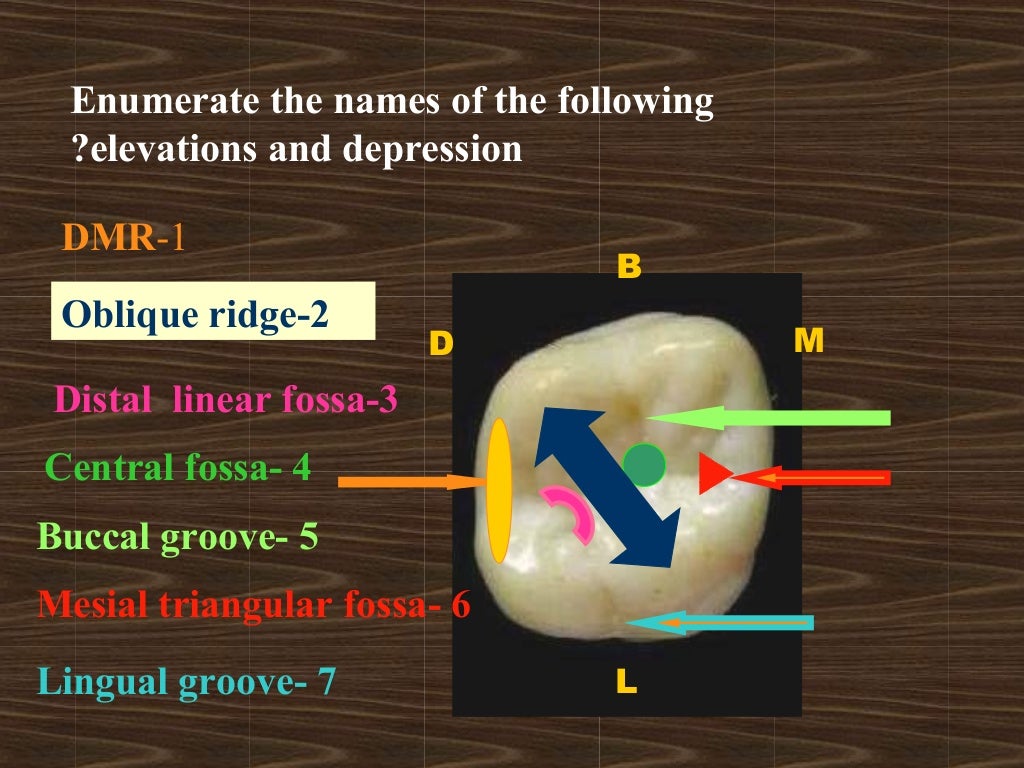
maxillary first molar
The maxillary first molar has a number of root concavities and furcations. The deeper concavities are located on the mesiobuccal root and, more frequently, on the palatal root. 4,6 Careful exploring is needed to detect residual deposit on these surfaces. Horizontal strokes or the use of a mini Gracey may help to remove calculus lodged in grooves.

Type traits that differentiate maxillary second from first molars Pocket Dentistry
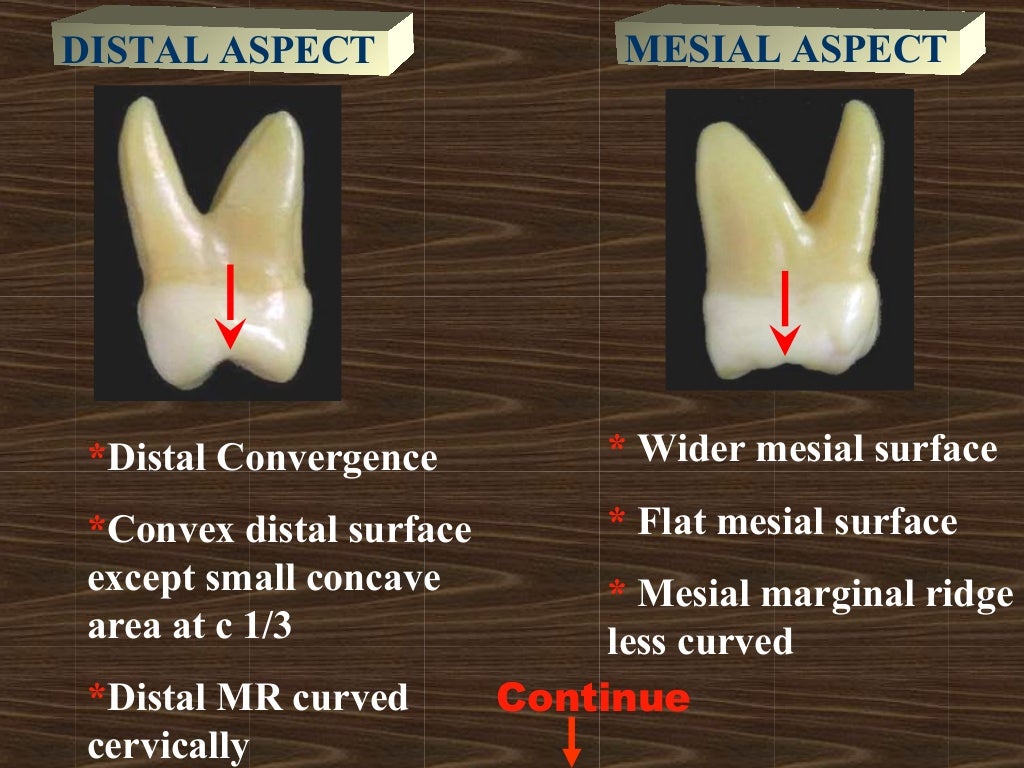
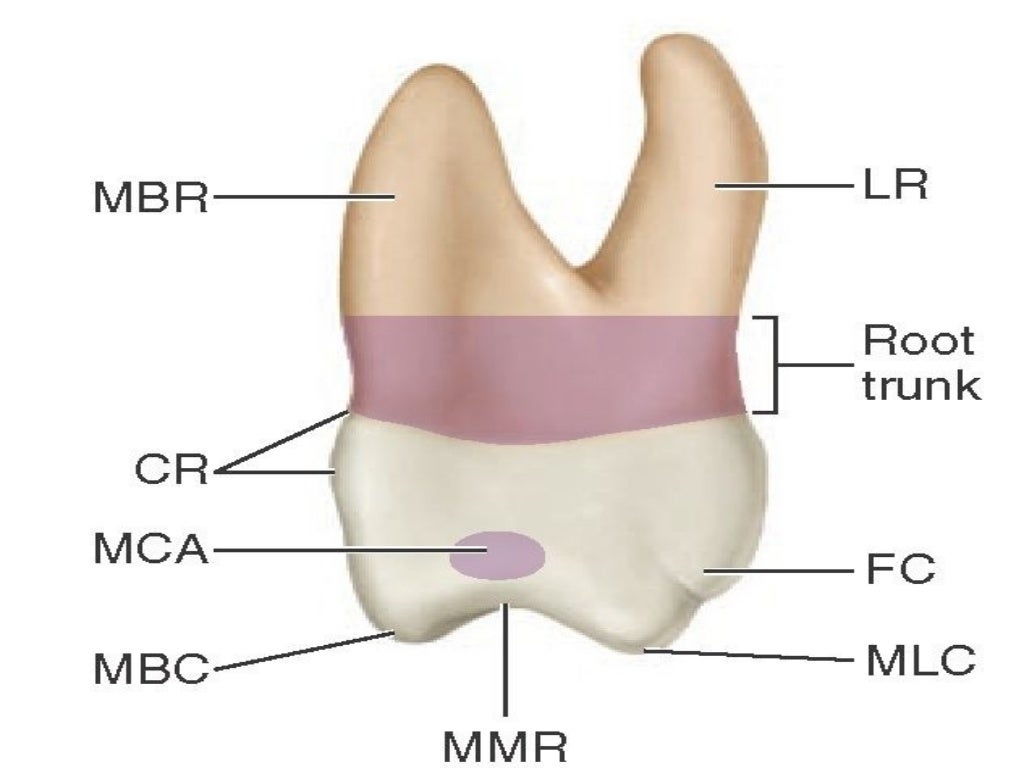
The maxillary first molar tooth is one of the three molar teeth that are found in a quadrant of the maxillary dental arcade. It includes the following bony features: - parts: crown, root, and cervical line; - surfaces: buccal, lingual, mesial, distal, and occlusal surfaces;
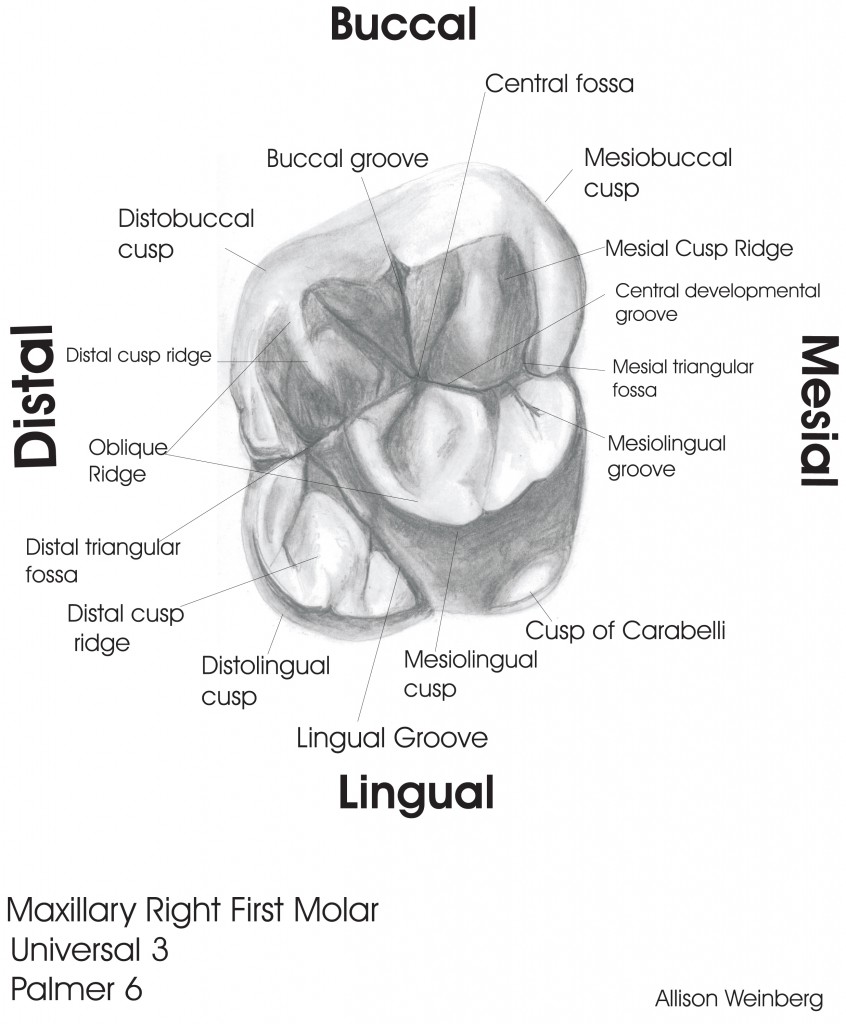
Sample Drawings Tooth Morphology
There are 4 major types of canal systems in the mesiobuccal root of the maxillary first molar: type I, single canal from pulp chamber to apex; type II, 2 separate canals leaving the pulp chamber, but merging short of the apex to form a single canal (Figures 2 and 3); type III, 2 separate canals leaving the chamber and exiting in separate foramin.
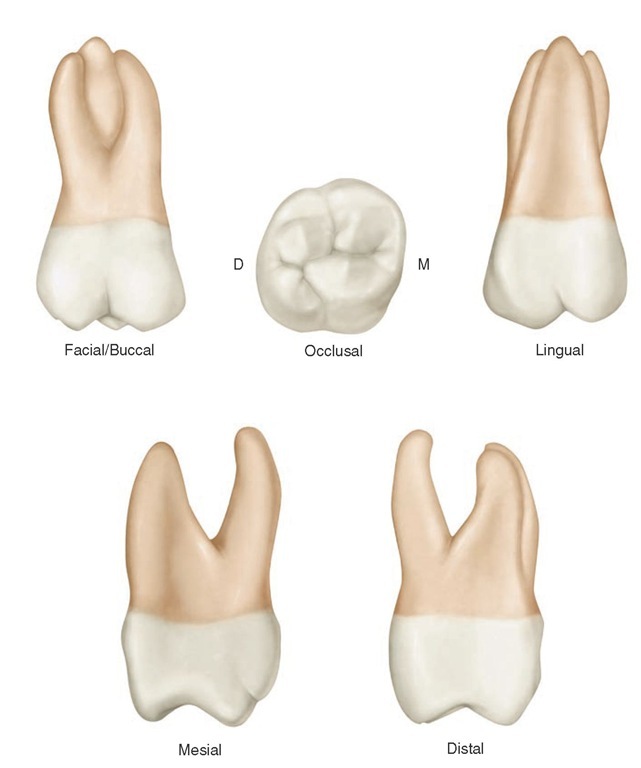
Review of Tooth Morphology (Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion) Part 2
Maxillary right permanent first molar to maxillary left deciduous second molar: UR6-ULE: Open in a separate window. Palatal expansion was simulated by applying transverse expansion forces to the maxillary right deciduous first molars (URD) and second molars (URE) or the maxillary permanent first molars (U6) on both sides of the palate.
The Root Canal Anatomy Project Maxillary First Molar
The maxillary first molar (see figure 4-25) is the largest tooth in the mouth. It develops from four lobes and is often called the "six year molar" because of the age at which it erupts. a. Facial Surface. The facial surface is convex in all directions.
maxillary first molar
The first maxillary molar is the only tooth of the maxillary molars, which sometimes has a 5th cusp called the cusp of Carabelli . The cusp of Carabelli is usually connected with the mesiolingual cusp. Also, the 5th cusp groove is usually present. The highest point of each cusp is known as the cusp apex .
The Root Canal Anatomy Project Maxillary First Molar MB2
The maxillary first molar is the largest tooth in the maxillary dental arch. The tooth has four well-developed cusps and one accessory or supplementary cusp called the cusp of Carabelli. The maxillary first molar has three well-developed roots. It erupts posterior to the deciduous maxillary second molar.
The Root Canal Anatomy Project Maxillary First Molar
The first maxillary molars have the following numbers according to different dental notation systems: 3 and 14 ( Universal Tooth Numbering System) 16 and 26 ( ISO-3950 system) 6⏌and⎿6 ( Palmer system) The numbers of the second maxillary molars are as follows: 2 and 15 (Universal Tooth Numbering System) 17 and 27 (ISO-3950 system)

Maxillary First Molar Root Canal Anatomy
The Maxillary First Molar Region. The posterior maxilla has been described as the most difficult and problematic intraoral area for implant placement. Both anatomic features and mastication dynamics contribute to the challenge of placing implants in this region. Anatomic factors in the maxillary first molar region include decreased bone.
Sterling Smiles Azle Difference between Maxillary and Mandibular molars
Permanent maxillary and mandibular first molars are the first permanent teeth to erupt into the oral cavity along with the mandibular incisors. It serves as an excellent record of maternal and fetal health, reflecting the prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal health and diseases.
maxillary first molar
The maxillary first molar is the human tooth located laterally (away from the midline of the face) from both the maxillary second premolars of the mouth but mesial (toward the midline of the face) from both maxillary second molars .