Overview of the Central Nervous System (Gross Anatomy of the Brain) Part 1
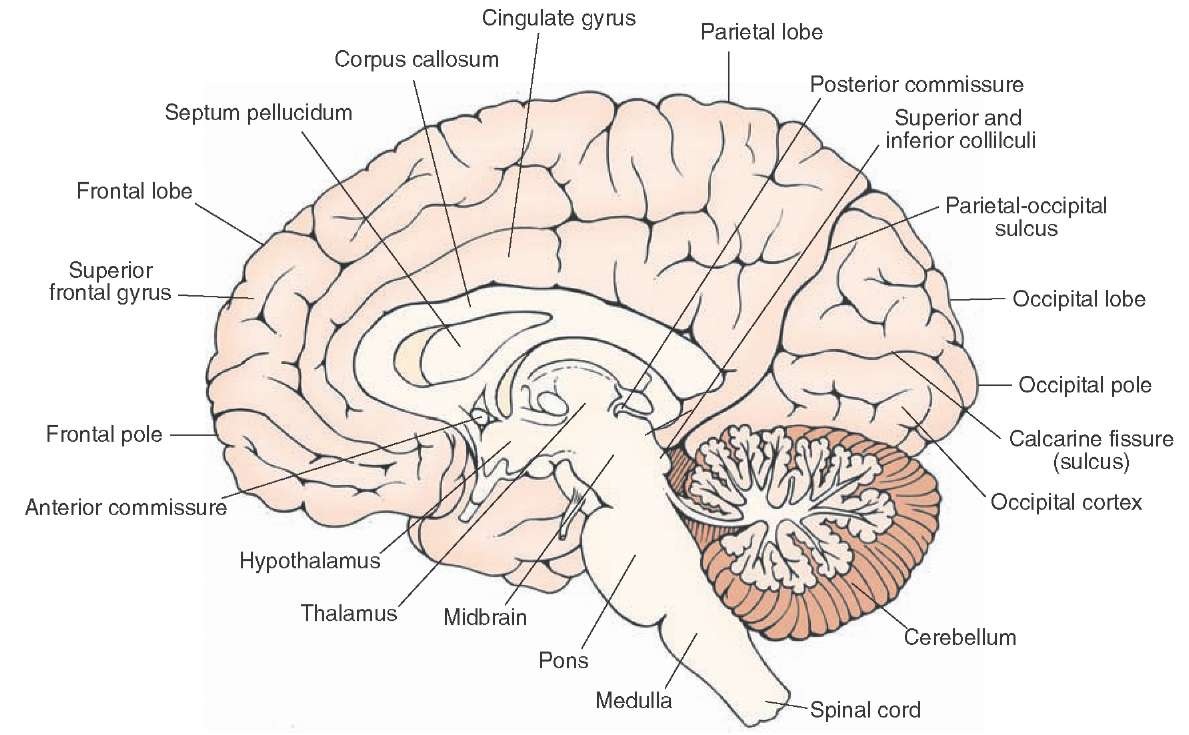
Figure 18.1. A midsagittal section of the brain. All four cerebral lobes are visible, as in the cingulate gyrus, which extends through the medial aspects of the frontal and parietal lobes. The corpus callosum sits beneath the cingulate gyrus. Below the cerebrum lies the midbrain, pons, medulla and cerebellum.

Midsagittal section of the brain. The Central Nervous System
the sagittal midline is observed when the cerebral aqueduct can be seen draining the third ventricle into the fourth ventricle. any displacement, of the cerebellar tonsils, or crowding of the foramen magnum. a review of the cisterns is important to note any displacement of the midline. moving superiorly, the cerebral aqueduct is observed for.

Midsagittal Section Of The Brain bmpwabbit
3. Mid-sagittal aspect of the brain. Now, let's briefly turn our attention to a single cerebral hemisphere. When the brain is cut in the midsagittal plane, all of its subdivisions are visible on the cut surface (see Figure 1.5B). Just as in the embryo, the subdivisions are arranged as though they were stacked, with the cerebral hemisphere.

Midsagittal Section Of The Human Brain Anatomy Body List Human Brain
The midsagittal section of the brain shows the three major parts of the brain, which are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.The cerebrum (prosencephalon or forebrain) comprises the telencephalon (cerebral hemispheres) and the diencephalon.They are each also divided into subparts or regions for simplified localization of structures, for example, the brainstem is composed of the midbrain.

Brain Structure Differentiation Introduction to Neuroscience
In this study, midsagittal brain shape variation is investigated in a sample of 102 humans, in order to describe and quantify the major patterns of correlation between morphological features, the effect of size and sex on general anatomy, and the degree of integration between different cortical and subcortical areas.

Midsagittal Section Of The Brain bmpwabbit
brainstem are visible on the medial surface of a brain that has been cut in the midsagittal plane. Parts of all of the subdivisions are also visible from the ventral surface of the whole brain. In this set of tutorials, you will find video demonstrations (from the brain anatomy lab) and photographs (in the tutorial notes)

Midsagittal Section Of The Brain bmpwabbit
Midsagittal section of the deep brain anatomy. This midline view demonstrates the third ventricle, with its roof formed by the body and column of the fornices and the velum interpositum. In the midline anteriorly, the lamina terminalis, optic chiasm and pituitary infundibulum are visible. The floor of the third ventricle is composed of the.

Midsagittal Section Of The Human Brain Chapter 12 The Central
All components of the ventricular system, except perhaps for the lateral ventricles, can be seen on a typical medial surface of the brain cut in the midsagittal plane. In Figure 1.12 , the lateral ventricle is visible in this hemisphere because the septum pellucidum has been dissected away; this is a very thin structure made of ependymal cells.
A midsagittal section of the human brain showing the inside surface
The midsagittal section of the brain shows the three major parts of the brain, which are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. The cerebrum (prosencephalo.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7668/medial-view-of-the-brain_english.jpg)
Midsagittal section of the brain Anatomy Kenhub
Brain, midsagittal view. Three views of brainstem. Top and anterior views of cerebellum. Major nuclei of thalamus. Lateral and medial surfaces of cerebrum, showing major sulci and gyri.. Anatomy Brain Anatomy; 2003/viewarticle/998119. A New Era in the Management of GERD 1.0 CME / CE / ABIM MOC Credits.
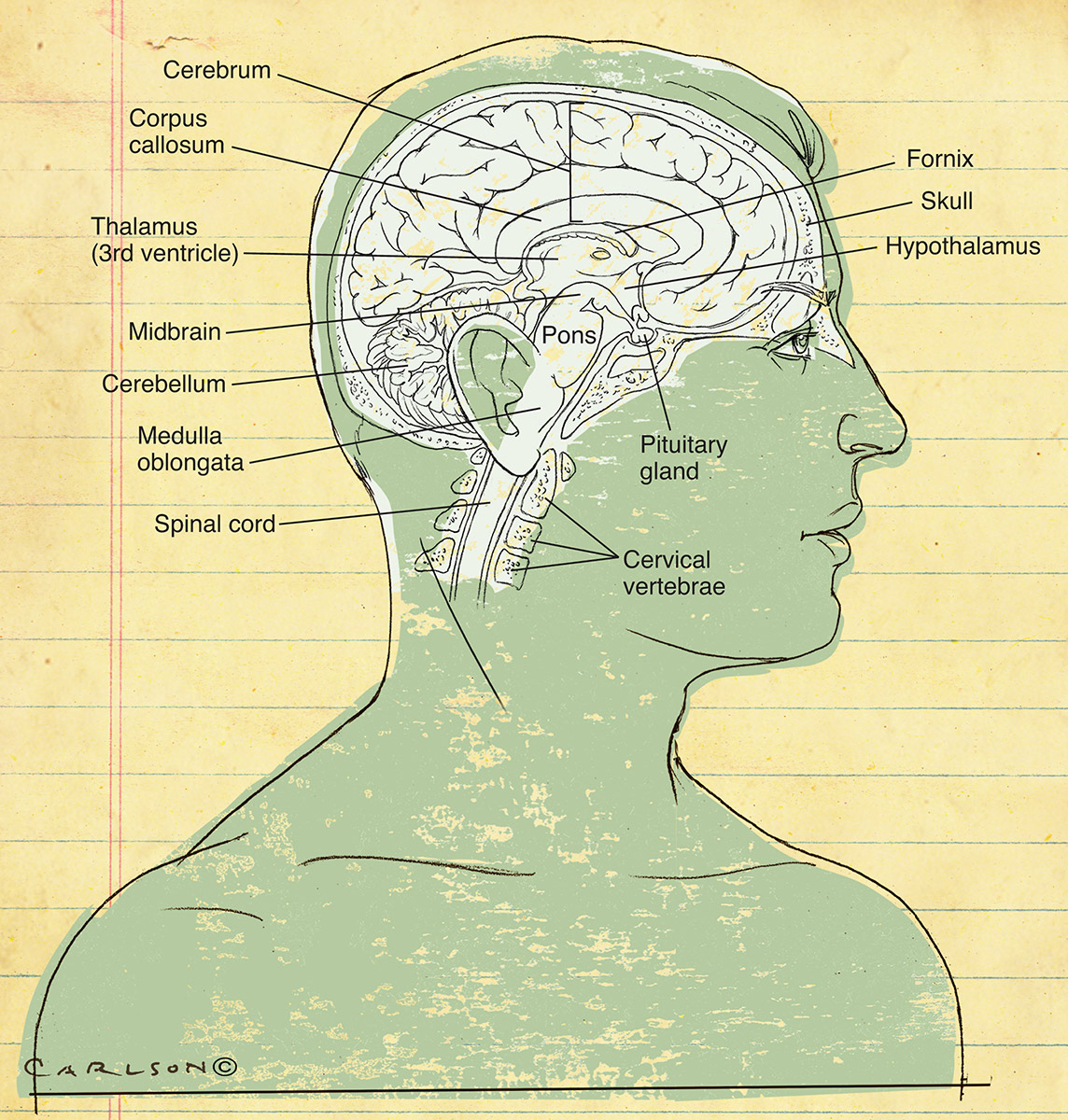
Human Brain Anatomy Midsagittal Carlson Stock Art
The thalamus is located deep in the brain. It can be seen in the midsagittal section in the area of the third ventricle. Many pathways between the cerebrum, brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord have a synapse in the thalamus.. The UBC Functional Anatomy images show the white and grey matter with its typical coloration. A list of the.

brain midsagittal view labels
Brainstem: Anatomy: The brainstem is divided into 3 sections: the midbrain (mesencephalon), the pons (metencephalon), and the medulla oblongata (myelencephalon) Function: The brainstem is responsible for swallowing, breathing, vasomotor control (blood pressure) the senses - taste, smell, hearing, touch, sight, and controlling heartbeat.

BrainMidsagittal Section Diagram Quizlet
Welcome to the Midsagittal Brain Study Module Page! Below you will find links to modules designed to help you learn all about the structures of the brain visible from a midsagittal section. In the Human Brain Anatomy Study Module , the parts of the brain are taken apart and put back together to help teach you about the structure and function of.

sagittal view of the human brain BRAIN SAGITTAL Anatomy
Midsagittal images of the brain provide a wealth of anatomic information and may show abnormalities that are pathognomonic for particular diagnoses. Using an anatomy-based approach, the authors identify pertinent anatomic structures to serve as a checklist when evaluating these structures. Subregions evaluated include the corpus callosum, pituitary gland and sellar region, pineal gland and.
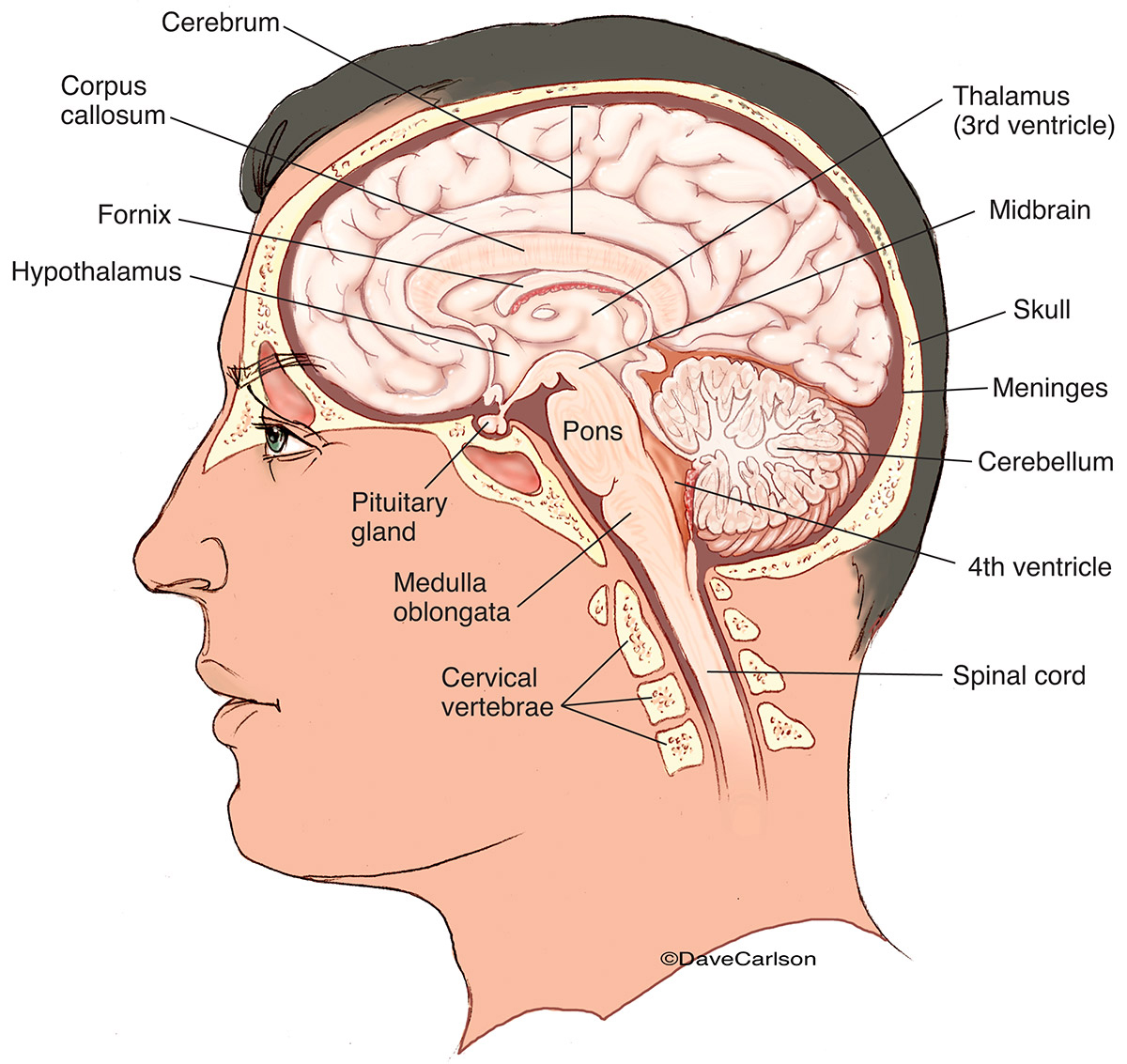
Human Brain Midsagittal View Carlson Stock Art
When the brain is hemisected in the midsagittal plane, all of its major subdivisions plus a number of additional structures are visible on the cut surface (Figure 1.14). In this view, the cerebral hemispheres, because of their great size, are still the most obvious structures. The frontal lobe of each hemisphere extends forward from the central sulcus, the medial end of which can just be seen.
Midsagittal Section Of The Brain Diagram Ajor Png
Several recent studies of psychiatric patients have relied upon magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to demonstrate features of cerebral anatomy in the midsagittal plane. Methodologies have varied somewhat in relation to thickness and position of planes of view. Due to concerns over the effects of slice.